Article
2024 Aug 05
Challenges Faced by Bariatric Patients in Pressure Injury Prevention
A specialized pressure relieving support surface solution effectively improves caregivers' workflow efficiency, accuracy, and handling injury risks and pressure injury prevention, comfort, and outcome for bariatric patients.
Bariatric Patients and Pressure Injury Risks
Bariatric patients, due to their increased body weight and associated health complications, are at a heightened risk of developing pressure injuries. In 2022, 43% of adults aged 18 years and over were overweight, and 16% were living with obesity.1 This rising prevalence highlights the importance of addressing the unique challenges faced by bariatric patients. Morbidly obese patients are three times more likely to develop pressure injuries than healthy individuals.2
Contributing Factors to Pressure Injuries
Several factors contribute to the increased risk of pressure injuries in bariatric patients:3
Friction and Shear Force
Friction occurs when the skin rubs against another surface, such as bedding or clothing. This can damage the outer layer of skin, making it more susceptible to pressure injuries. Shear force, on the other hand, happens when the skin moves in one direction while the underlying bone moves in another, causing distortion of the skin and underlying tissues.
An increased tissue weight exerts additional load on dependent tissues and causes vascular occlusion and tissue deformation. Shear and friction are often increased when individuals with bariatric needs tend to drag their heels and sacrum while getting out of bed.
Poor Microclimate
A poor microclimate around the skin, characterized by excessive moisture and heat, can further elevate the risk of pressure injuries. Bariatric patients often have large skin folds that trap moisture and heat, creating an environment conducive to skin maceration, inflammation, and breakdown. Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers/Injuries: Clinical Practice Guideline 2019 strongly advises proper skin microclimate management to reduce pressure injury risks.
Inadequate Bed Size
Standard hospital beds are often too small to accommodate bariatric patients comfortably. This inadequacy can lead to increased pressure points and discomfort, further elevating the risk of pressure injuries. The lack of appropriate supportive equipment and adequate resources interferes with implementing preventative measures for bariatric care4. Beds designed specifically for bariatric patients, which provide adequate support and pressure relieving, are essential in mitigating these risks.
Challenges for Healthcare Providers
Caring for bariatric patients presents significant challenges for healthcare providers. The physical effort required to reposition and transfer bariatric patients can lead to musculoskeletal injuries among caregivers. Additionally, the need for specialized training and equipment adds complexity to the care process5. Ensuring the safety and well-being of both patients and caregivers requires dedicated resources and protocols.
Explore the Impact of Pressure Injuries on Your Hospital
Advanced Support Surfaces for Bariatric Pressure Injury Prevention.
Here are the key benefits it provides:
- Enhance care process : Auto adjustment function simplifies care delivery by optimizing mattress firmness according to the patient's weight.
- Special design wilder size: Wider, sturdier mattress improves pressure redistribution coverage and injury risks.
- Microclimate management: Micro low air loss wicks moisture from patients' skin and improves skin microclimate control.
- Extra protection with sacral area cushioning : Structurally reinforced air cells in the torso section provide support and comfort during sitting.
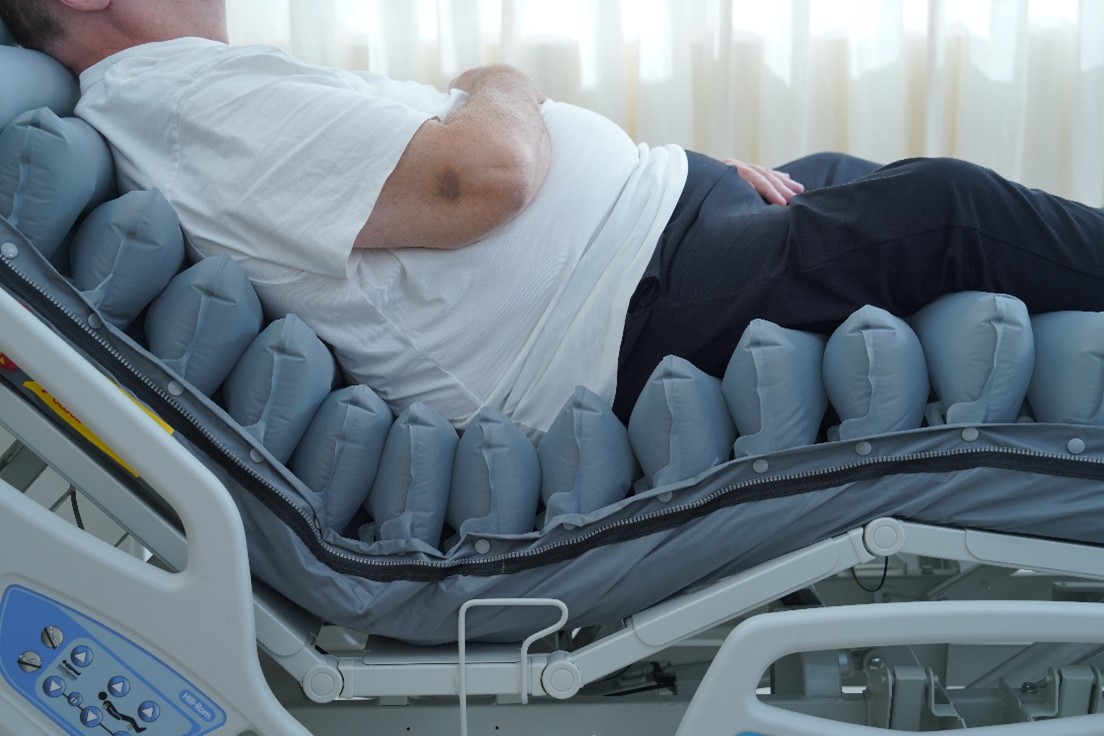 Figure1:Special air cell design and settings ensure that bariatric patients do not bottom out while seated.
Figure1:Special air cell design and settings ensure that bariatric patients do not bottom out while seated.
For more information on how specialized support surfaces can help in pressure injury prevention and enhance patient care, visit Wellell.
Pro-care Auto Bariatric Pro-care Auto Bariatric - Support Surfaces - Pressure Area Care | Wellell
Explore the Impact of Pressure Injuries on your hospital
- Discover the range of Wellell's pressure relief mattresses
Pressure Relief Mattress: Support Surfaces|Wellell
Resources:
- Obesity and overweight. World Health Organization. Accessed 08/05/2024
- Ness SJ, Hickling DF, Bell JJ, Collins PF. The pressures of obesity: The relationship between obesity, malnutrition and pressure injuries in hospital inpatients. Clin Nutr. 2018 Oct;37(5):1569-1574. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Aug 19. PMID: 28890276.
- Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers/Injuries: Clinical Practice Guideline. The International Guideline. Emily Haesler (Ed.). EPUAP/NPIAP/PPPIA; 2019.
- Health Survey for England, 2018: Quick guide. (2019, December 3). Health Survey for England 2018 [NS] - NHS Digital. NHS Digital. https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/health-survey-for-england/2018
- Choi, S. D., & Brings, K. (2015). Work-related musculoskeletal risks associated with nurses and nursing assistants handling overweight and obese patients: A literature review. Work (Reading, Mass.), 53(2), 439–448. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-152222

